Theme: Reconstruction of big amputations of 1/3 part of upper auricular with graft from nasal septum in two stages. (Skin Flap Pocket Technique)
1Gjergji Bizhga, 2 Xhevair Hoxhallari, 3Melpomeni Kromidha.
1SQUT , Tirane, Albania
2QSUT Nene Tereza, Tirane, Albania
Abstract
Background: Various reconstructive techniques for partial traumatic ear amputations have been reported. The choice of technique is based on the missing ear components and the availability of tissue for defect coverage.
The goal is to obtain an aesthetically acceptable ear. The authors report a two-stage skin flap pocket technique for the reconstruction of traumatic ear amputations.
Patient and Method: We present two cases of partial traumatic ear amputation due to bite from a human being. Graft from the nasal septum is taken in both cases after performing a septoplasty. After taking cartilaginous graft from septum, an refreshments of the edges of amputation is performed and fixation of the graft with the cartilage of auricle in the place of amputation and then its insertion with auricle cartilage in amputation location and insertion in subcutan retroauricular pocket
Both cases underwent to a second intervention after three months, where dislocation from retroauricular region, dislocation of auricle is performed and its modeling.
Results: In 2 months follow-up, all of 2 cases showed no signs of infection. Normal dimension of the ears were achieved and aesthetic appearances were perceived as acceptable to the patients and other viewers. One patient
was able to be followed one year post surgery with acceptable aesthetics, and no sign of cartilage absorption.
Summary: The technique used in these cases provided acceptable results in reconstructing the size and shape of the partially amputated ears. Septal cartilage grafts implanted in the pockets retained their shape with no infection or absorption.
Keywords: Ear amputation, partial ear amputation, pocketing technique, men-bite to the ear, septal graft
Introduction
Traumatic partial amputations of auricle is favorised from exposed position of the ear related to the head. Reconstruction of partial amputations presents difficulties related to the architecture and structure of auricle, when we have a fragile cartilage and thin skin. Different interventional techniques are use to repair the defect.. Expander of damage and the defect itself are decisive factors in choosing the mode of reparation.
Upper part, middle part or lower part must be the amputated part. Amputations in vertical plan must encompass only helix, but antihelix may be compromised as well. Direct reparation is performed when a loss smaller then 1or 2 cm is missing. When we face bigger amputations we need a reparation and reconstruction plan 1,2]
Bigger defects must be corrected using amputated cartilage, cartilage from ear s chonchaes of the other ear, cartilage from the rib, or nasal septum cartilage. In this kind of defects auricles reparation is done in two steps. First phase is taking the graft and adapting with amputated part, inserting in retro auricular region and the second phase is dislocation and final modeling.
Material and method
Two patients 36 and 43 years old, male gender underwent to surgery, where graft is taken from nasal septum cartilage and method “Skin Flap Pocket Technique” is used.
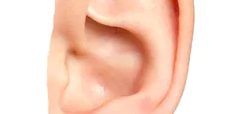
Both they presented old amputation of ear helix, one of the left ear (fig. 1) and the other of the right ear (fig 2). The missing edge varied from 4-5 cm long and 1.5 -2,5 wide.
The cause of amputation was the bite from another human being. Graft was taken from nose cartilage and they had septoplasty because of a deviation of septi nasi.
On the first phase we performed septoplasty and we took cartilage septum, refreshment of amputated region edges and fixation of graft with residual cartilage of auricle. In retroauricular region was created a subcutan pocket in sizes of graft. We did adaptation of graft in fosse retroauriculare, suturing skin in amputation level.(
Second phase was started three months after skin and graft vitalization happened, then we did dislocation and auricle remodeling. (Fig.2,5) .
On the end of the second phase auricle was modeled, in order to reach the shape and anatomical size.(Fig. 3). Removing stitches stared on 10 th day and continued to 14 th day. Following up this cases after a month and later on, the auricle took the a very good anatomical and esthetical shape
Patients were satisfied too. Results have been esthetically sustainable esthetically and no graft absorption was noticed in both cases (the first one I 5 years and the second one in one year . (Fig. 6).Another bonus was improvement of nose breathing.
Figura 1.Right old partial ear amputation. Figura 2.Septal graft buried in the retroauricular skin flap pocket 3 months after firs stage technique